desired language:
desired language:
SDK 101
The Decentraland SDK is a powerful tool that lets you create scenes by writing code.
Install the CLI
To get started, install the Command Line Interface (CLI).
The CLI allows you to compile and preview your scene locally. After testing your scene locally, you can use the CLI to upload your content.
Note: Install the following dependencies before you install the CLI:
- Node.js (version 8 or later)
To install the CLI, run the following command in your command line tool of choice:
npm install -g decentraland
Read Installation guide for more details about installing the CLI.
Create your first scene
Create a new scene by going to an empty folder and running the following command line command:
dcl init
Preview the 3D scene in your browser by running the following command in that same folder:
dcl start
Read more about the scene preview in preview a scene
Edit the scene
Open the src/game.ts file from your scene folder with the source code editor of your choice.
Tip: We recommend using a source code editor like Visual Studio Code or Atom. An editor like this helps you by marking syntax errors, autocompleting while you write and even showing smart suggestions that depend on context. Also click on an object to see the full definition of its class.
/// --- Set up a system ---
class RotatorSystem {
// this group will contain every entity that has a Transform component
group = engine.getComponentGroup(Transform)
update(dt: number) {
// iterate over the entities of the group
for (let entity of this.group.entities) {
// get the Transform component of the entity
const transform = entity.getComponent(Transform)
// mutate the rotation
transform.rotate(Vector3.Up(), dt * 10)
}
}
}
// Add a new instance of the system to the engine
engine.addSystem(new RotatorSystem())
/// --- Spawner function ---
function spawnCube(x: number, y: number, z: number) {
// create the entity
const cube = new Entity()
// set a transform to the entity
cube.addComponent(new Transform({ position: new Vector3(x, y, z) }))
// set a shape to the entity
cube.addComponent(new BoxShape())
// add the entity to the engine
engine.addEntity(cube)
return cube
}
/// --- Spawn a cube ---
const cube = spawnCube(5, 1, 5)
cube.addComponent(
new OnClick(() => {
cube.getComponent(Transform).scale.z *= 1.1
cube.getComponent(Transform).scale.x *= 0.9
spawnCube(Math.random() * 8 + 1, Math.random() * 8, Math.random() * 8 + 1)
})
)
Change anything you want from this code, for example change the x position of the first cube entity that’s spawned. If you kept the preview running in a browser tab, you should now see the changes show in the preview.
Download this 3D model of an avocado from Google Poly in glTF format. link
Create a new folder under your scene’s directory named /models. Extract the downloaded files and place them all in that folder.
At the end of your scene’s code, add the following lines:
let avocado = new Entity()
avocado.addComponent(new GLTFShape("models/avocado.gltf"))
avocado.addComponent(
new Transform({
position: new Vector3(3, 1, 3),
scale: new Vector3(10, 10, 10),
})
)
engine.addEntity(avocado)
Check your scene preview once again to see that the 3D model is now there too.
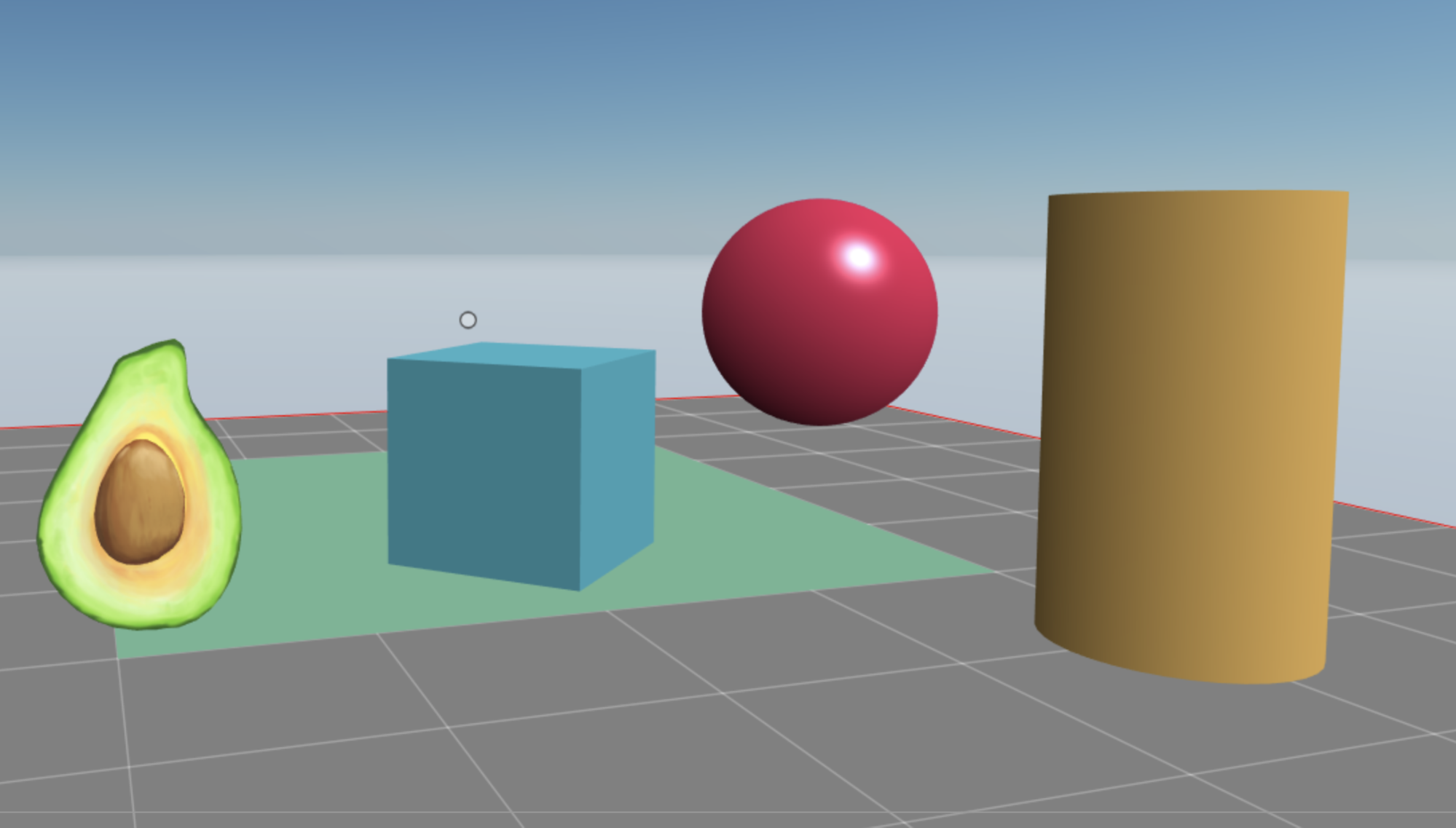
The lines you just added create a new entity, give it a shape based on the 3D model you downloaded, and set its position and scale.
Note that the avocado you added rotates, just like all other entities in the scene. That’s because the RotatorSystem system that was defined in the default code of this scene is iterating over every entity in the scene and rotating it.
Read coding-scenes for a high-level understanding of how Decentraland scenes function.
See the Development guide section for more instructions about adding content to your scene.
Publish your scene
Once you’re done creating the scene and want to upload it to your LAND, see publishing.
More Tutorials
Read our tutorials or view or video tutorials for detailed instructions for building basic scenes.
To see our official example scenes, with links to their code, see scene examples.
Engage with other developers
Visit Discord, join a lively discussion about what’s possible and how!
To debug any issues, we encourage that you post issues to Stack Overflow, using the tags decentraland or decentraland-ecs.
You can also ask in Discord. The #developers channel is for questions regarding code, the #building channel is for questions regarding 3D models and art.
The Utils library
The Decentraland ESC Utils library includes a number of helper methods that make it easier to carry out a lot of common use cases.
To use any of the helpers provided by the Utils library:
-
Install it as an npm package. Run this command in your scene’s project folder:
npm install decentraland-ecs-utils -
Import the library into the scene’s script. Add this line at the start of your
game.tsfile, or any other TypeScript files that require it:import utils from "../node_modules/decentraland-ecs-utils/index" -
In your TypeScript file, write
utils.and let the suggestions of your IDE show the available helpers.
Read the full documentation of the Utils library here
3D Art Assets
A good experience will have great 3D art to go with it. If you’re keen on creating those 3D models yourself, you’re encouraged to, see the 3D Modeling section of our docs for more info. But if you prefer to focus on the coding or game design side of things, you don’t need to create your own assets!
Here are a few tips to get great 3D models that you can use in a Decentraland scene:
- Build a scene in the Decentraland Builder and export it, together with all its assets, to keep working on it with the SDK.
- Download all the 3D assets available in the Builder from this repo
- Google Poly
- SketchFab
- Clara.io
- Archive3D
- SketchUp 3D Warehouse
- Thingiverse (3D models made primarily for 3D printing, but adaptable to Virtual Worlds)
- ShareCG
Note: Models must be in the supported
.gltfor.glbformats, and must have a number of triangles, textures and materials that adhere to the scene limitations. If getting models from a third party site, pay attention to the licence restrictions that the content you download has.